NICT, KIYOHARA OPTICS, ArkEdge Space and SoftBank Corp. Enter Collaborative Agreement to Demonstrate Optical Wireless Communications Between Space and the Stratosphere
– Four parties will verify bidirectional communication by equipping optical wireless communication devices on Low Earth Orbit satellites and HAPS –
The National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (hereinafter “NICT”), KIYOHARA OPTICS Inc. (hereinafter “KIYOHARA OPTICS”), ArkEdge Space Inc. (hereinafter “ArkEdge Space”), and SoftBank Corp. (hereinafter “SoftBank”) have entered into a collaborative agreement to advance the demonstration of optical wireless communications between space and the stratosphere, as well as between space and the ground.
The four parties will collaborate on the development of optical wireless communication devices and their application to both satellites and stratospheric communication platforms (High Altitude Platform Stations, hereinafter “HAPS”).
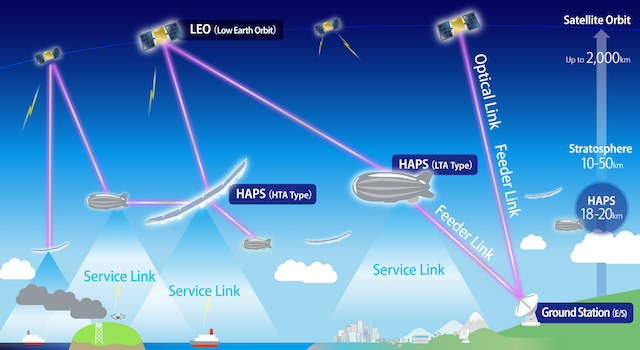
The first demonstration will target a launch of a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite in 2026 to verify optical wireless communications between space and the ground. Furthermore, in 2027, the parties aim to conduct a world-pioneering initiative by mounting optical wireless communication devices on HAPS to verify bidirectional optical wireless communications between space and the stratosphere.
Background of the Demonstration
In recent years, optical wireless communications have attracted attention as a next-generation high-speed communication technology to support non-terrestrial networks (NTN) such as satellite communications and HAPS. While already in practical use for inter-satellite links, the technology is expected to contribute to the immediate relay of Earth observation data, connectivity in underserved areas, rapid restoration of communications in disaster situations, and low-latency intercontinental backbones, thereby enabling fast, large-capacity, and flexible network deployments.
Unlike radio waves, optical wireless communications use light, eliminating the need for frequency allocation and wireless licenses, while offering high-speed connectivity. However, since the technology relies on ultra-narrow, highly directional beams, establishing and maintaining stable communication is extremely challenging. In the 2027 demonstration, the parties will attempt bidirectional optical wireless communications between a HAPS stationed in the stratosphere and a LEO satellite orbiting the Earth at high speed, covering a distance of up to approximately 2,000 km—an ambitious and technically demanding undertaking.
Features of the Communication Devices and Satellites Under Development
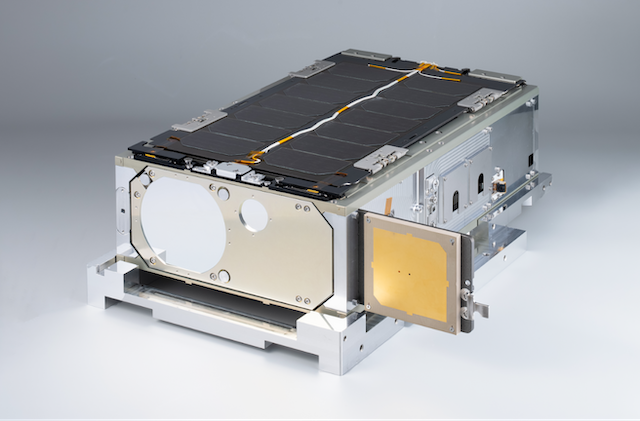
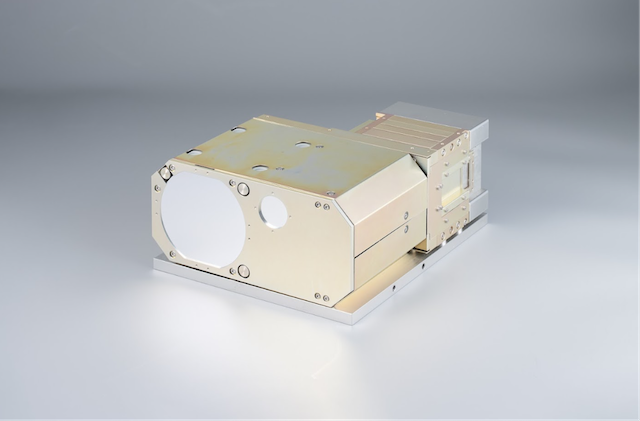
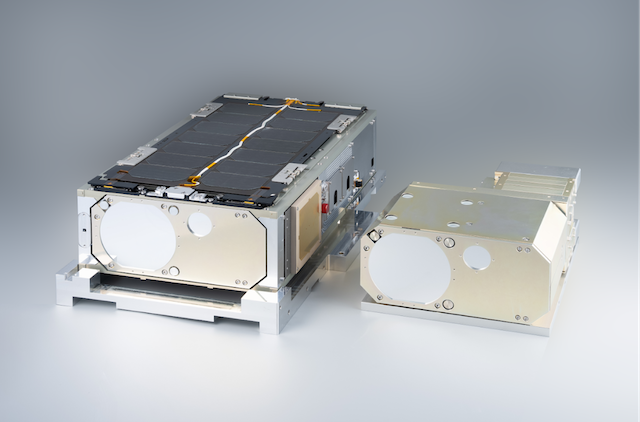
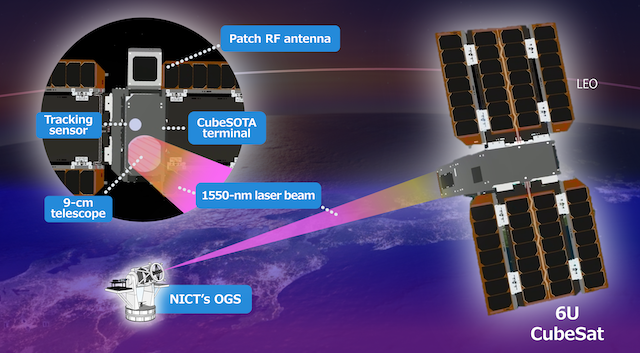
The optical wireless communication device currently under development is designed to be compact, lightweight, and energy-efficient, while enabling high-speed bidirectional communication at 10 Gbps. Enhancements are being made to ensure reliable operation in extreme environments, including radiation exposure in space and temperatures below -90°C in the stratosphere. The demonstration satellite, currently in development, will be a 6U class CubeSat1. Based on a versatile satellite bus design, it will incorporate advanced attitude control technologies required to support optical wireless communications.
Note1: CubeSat refers to a standardized small satellite format, where one unit (1U) is 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm. A 6U CubeSat is approximately 10 cm × 20 cm × 30 cm in size.
Roles of the Four Parties
- NICT: Development of optical wireless communication devices suitable for space and stratospheric environments, link design through the atmosphere, and development/operation of ground optical stations.
- KIYOHARA OPTICS: Development and manufacturing of optical wireless communication devices for satellite and HAPS deployment.
- ArkEdge Space: Design and development of micro-satellite bus, launch coordination, and satellite operations.
This satellite, currently under development by ArkEdge Space, was initially adopted with the support of Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) in FY2021 and has been further promoted as part of the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO)’s research and development program since FY2023.
This satellite, currently under development by ArkEdge Space, was initially adopted with the support of Japan’s Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) in FY2021 and has been further promoted as part of the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO)’s research and development program since FY2023.
- SoftBank: Development of optical wireless communication devices and related equipment for stratospheric environments, as well as HAPS flight operations and integration of equipment.
For more information on optical wireless communications in NTN, please refer to the blog article by SoftBank’s Advanced Technology Research Institute.
For more information on optical wireless communications in NTN, please refer to the blog article by SoftBank’s Advanced Technology Research Institute.
About the Organizations
National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT)
NICT is Japan’s sole public research institute specializing in the field of information and communications technology (ICT). It conducts R&D comprehensively from basic to applied research, while actively collaborating with universities, industry, local governments, and domestic/overseas research institutes. NICT strives to return research results to society and foster innovation.
- - Established:
- April 2004
- - Headquarters:
- 4-2-1 Nukui-Kitamachi, Koganei, Tokyo
- - President:
- Hideyuki Tokuda
- - URL:
- https://www.nict.go.jp/en/
KIYOHARA OPTICS Inc.
KIYOHARA OPTICS has a 76-year history as a comprehensive optics manufacturer, specializing in the design and development of optical components for research, custom production of specialized optical parts, and consulting in optics. The company has contributed to space development through the manufacturing of space telescopes for Earth observation satellites, and the development of optical transceivers for LEO and HAPS optical communications.
- - Founded:
- April 10, 1949 (Incorporated: June 18, 1987)
- - Headquarters:
- 3-28-10 Funado, Itabashi, Tokyo
- - President:
- Hirohiko Shinonaga
- - URL:
- https://www.koptic.co.jp/opt/eng
ArkEdge Space Inc.
ArkEdge Space is a Japanese space technology company offering end-to-end solutions for micro-satellite constellations—from planning and design to mass production and operations. Guided by its mission of “empowering people with satellites for a prosperous future,” the company is advancing capabilities in Earth observation, maritime satellite communications (VDES), optical communications, and low-Earth orbit satellite positioning, as well as lunar activities and deep space exploration. Through our mission, ArkEdge Space continues to drive the advancement of space innovation and its practical application.
- - Established:
- July 2018
- - Headquarters:
- 3F, Dome Ariake HQ, 1-3-33 Ariake, Koto, Tokyo
- - CEO:
- Takayoshi Fukuyo
- - URL:
- https://arkedgespace.com/en
SoftBank Corp.
Under its “Beyond Carrier” strategy, SoftBank is going beyond the traditional telecommunications operator framework by leveraging advanced technologies such as AI, IoT, and 5G to create new businesses across industries and drive digital transformation (DX). Guided by its vision of “Ubiquitous Transformation (UTX),” SoftBank is working to integrate terrestrial mobile networks with NTN using satellites and HAPS to build a communication infrastructure that ensures seamless connectivity everywhere.
- - Established:
- December 1986
- - Headquarters:
- 1-7-1 Kaigan, Minato, Tokyo
- - President & CEO:
- Junichi Miyakawa
- - URL:
- https://www.softbank.jp/en
NICT Contact
TSUJI Hiroyuki
National Institute of Information and Communications Technology
E-mail: tsuji nict.go.jp
nict.go.jp
 nict.go.jp
nict.go.jp