“Time Business”
Electronic Time Authentication
The Japanese term "タイムビジネス", time business, describes the time authentication and time distribution services required for ensuring safety and reliability in a digital society.
The "e-documents law"[1] came into effect in Japan in April 2005 to address the need to store legal documents in electronic form rather than on paper. This law requires electronic documents to be time stamped in a way that shows they have not been altered. The Information Technology (IT) community has also been encouraged to adopt precise and accurate timing records everywhere.
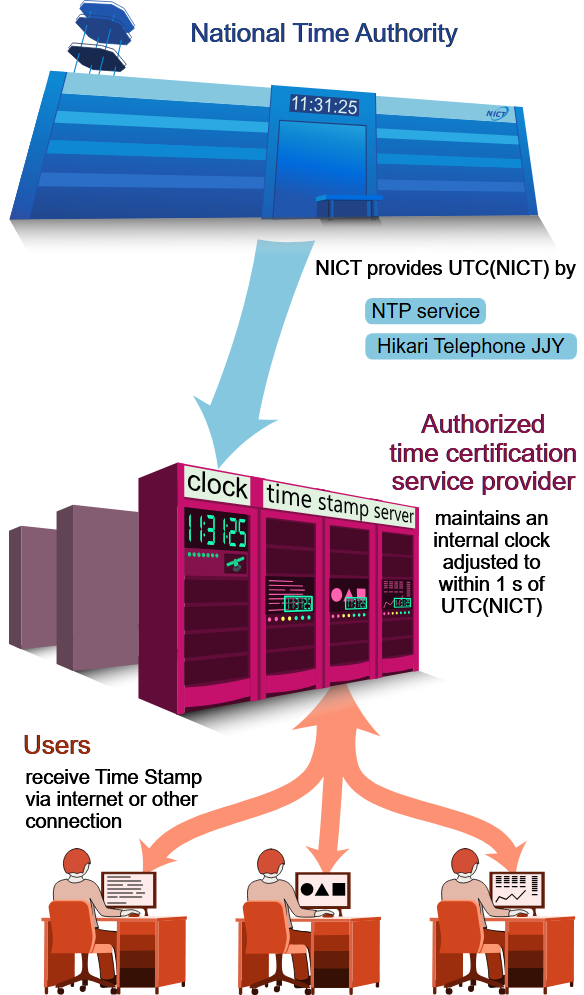
In February 2005[2] NICT began distributing Japan Standard Time (JST) in an easy-to-use format to respond to this need of society. Initially, the time stamps issued based on this time information were certified through a voluntary organization. However, a national certification system was launched in July 2021, in line with developments in other countries.
was launched in July 2021, in line with developments in other countries.
Within this system, NICT serves as the National Time Authority (NTA), and it provides JST and the underlying UTC(NICT) to authorized time certification service providers. This is often realized by Hikari Telephone JJY and Time Dissemination by Leased Line. The authorized providers are then responsible for maintaining their own timescale such that the difference between their clocks and Japan Standard Time remains within one second. This creates a system where the time stamps provided to users are traceable to JST.
To ensure that each step in this traceability chain is carefully examined and reliable, NICT continues to promote[3,4] the relevant national and international industrial standards, such as JIS X 5094 and ISO/IEC 18144.
Time Dissemination by Leased Line (NTP service)
Time dissemination by leased line is available for users that require access to the time information distributed by NICT’s NTP, but do not want to access it over the public internet. This service is intended for public institutions, certified time distributors, internet providers and other users with special requirements.
To realize access, a dedicated communications line will be established between NICT and the user’s site, creating a direct connection from NICT’s stratum 1 NTP server and a stratum 2 server on the user side.
While access to the NTP server is free, the user is required to provide the necessary equipment and is responsible for the cost of the connection and the installation of the required equipment at NICT. Applications are reviewed at the end of March, June, September and December, and following the review it will be necessary to conclude a contract with NICT.
Related documents
- Network time service (Time Dissemination by Leased Line) usage guide
Download (PDF, Japanese)
(PDF, Japanese) - Documentation for Time Dissemination by Leased Line service
・Application for use
・Connection information sheet
・Equipment requirements
・Contract
Download (PDF, Japanese)
(PDF, Japanese) - Annual report of operation for submission to NICT
Download (PDF, Japanese)
(PDF, Japanese)
Further Information
If you are looking for information on the previously offered services, please check the previous webpage . If you have urgent questions, please contact us directly at
. If you have urgent questions, please contact us directly at
jst-service .
.
References
1)
Use of Information and Communication Technology in the Storage of Documents Conducted by Private Businesses, etc.
Available at elaws.e-gov.go.jp (Japanese)
(Japanese)
2)
H. Saito,
Japan Standard Time and Time Business,
NICT News 344, 3 (2004)
(2004)
3)
T. Iwama, H. Saito, A. Machizawa and H. Toriyama,
Trend of Time Business in Japan,
Journal of NICT 57, 69 (2010)
(2010)
4)
T. Iwama,
Introducing Japan's Time-stamping Technologies to the Global Market,
NICT News 394, 1 (2010)
(2010)

